Pofol -Your Guide To A Relaxing Experience!
It helped me feel calm and comfortable before the procedure, and the recovery was smooth. Thanks to Pofol, the experience was much better than expected.
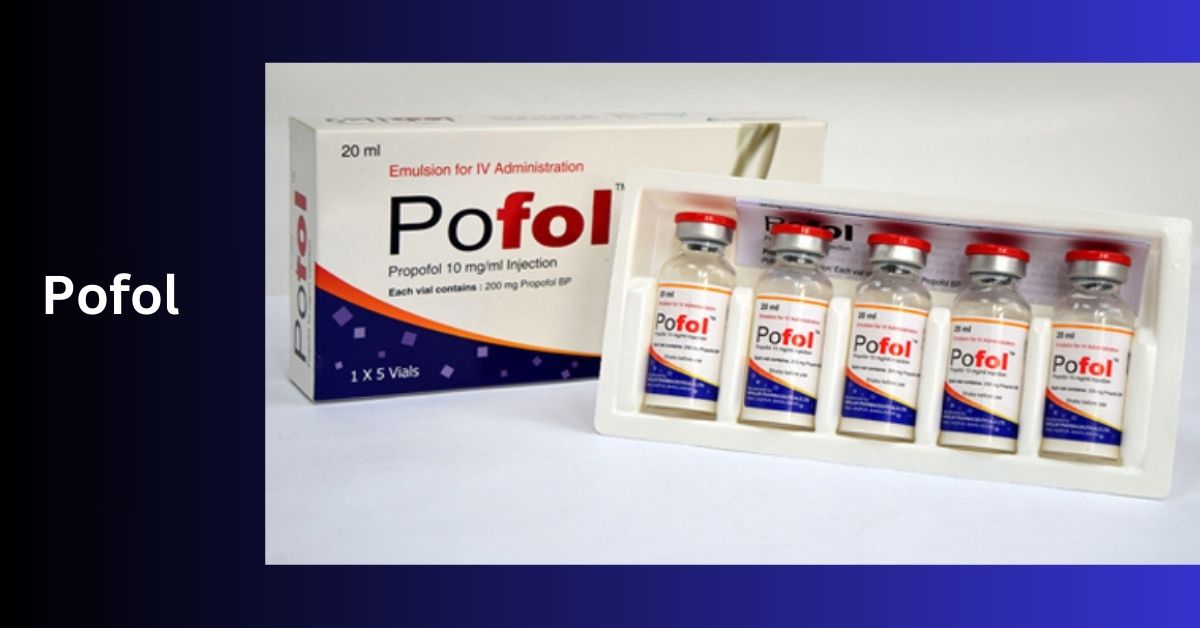
Pofol, or Diprivan, is a helpful medicine for calm and controlled experiences during medical procedures. It works quickly and is easy to trust, making the process smooth and worry-free. Count on Pofol for a comfortable and practical sedation experience.
In this article, we will explore Pofol, the helpful medicine that makes medical procedures easier. We discuss how Pofol, called Diprivan, works quickly and smoothly, ensuring your experience is comfy and stress-free.
What Is Pofol? – Let’s Find Out!
Pofol, short for Propofol, is a special medicine doctors use to help people with medical procedures. It’s a liquid that goes into your body through a tiny tube in your vein. Imagine it as a friendly superhero calming your body during surgeries or other treatments.
This superhero medicine works super fast, making you sleepy and comfortable before the doctor starts their work.
The cool thing is it wears off quickly, too, so you wake up feeling refreshed. It is like a sleepy-time friend for your body, ensuring you have a smooth and effortless experience when you need extra help at the hospital.
When Do We Use Pofol? – Understanding Its Applications!

Pofol is like a helpful superhero in the medical world; we use it in special times to make things easier for our bodies.
Imagine when someone needs surgery or a medical test – that’s when Pofol steps in. It’s given through a tiny tube in the vein to make the person feel relaxed and sleepy so they don’t feel any pain during the procedure.
Doctors also use Pofol in intensive care units (ICUs) when someone is on a breathing machine, ensuring they stay calm.
It’s versatile, appearing during surgeries and monitored anesthesia care (MAC) for specific medical tests. So, we use Pofol to keep things smooth and comfy during these essential moments in the hospital.
How Does Pofol Work? – Explore Now!
It works like a sleepy potion for your body. When doctors give you Pofol through a tiny tube in your vein, it quickly makes you feel relaxed and sleepy.
It’s like a gentle superhero calming down your body so you won’t feel anything during surgeries or medical treatments.
The magic of Pofol is that it slows down the busy signals in your brain, helping you doze off smoothly. Once the medical work is done, Pofol wears off fast, and you wake up feeling like you had a nice nap.
So, think of Pofol as a helpful friend who ensures you’re super comfy during medical stuff, and you won’t even notice the action happening around you.
How Much Pofol Do You Need? – Finding The Right Amount For Different Situations!
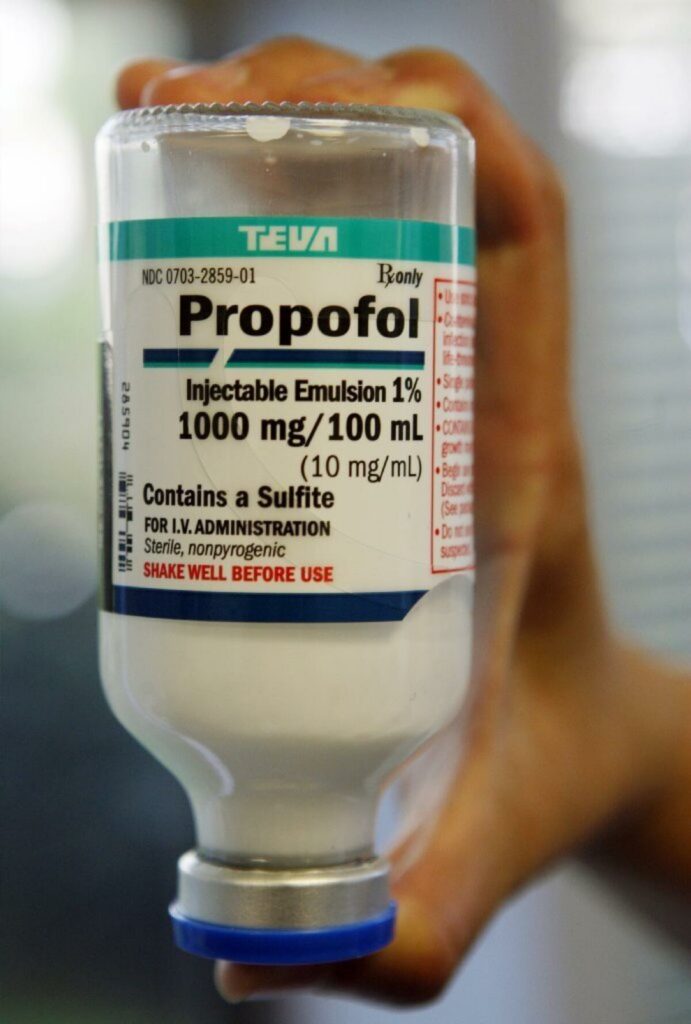
| Anesthesia Induction for Adults (Under 55 years – ASA I/II) | Pofol is given in 40 mg doses through IV every 10 seconds until the person starts feeling its effects. |
| Anesthesia Induction for Adults (Over 55 years or debilitated – ASA III/IV | A reduced dosage of 20 mg through IV every 10 seconds was used to prevent unwanted side effects. |
| Anesthesia Maintenance for Adults (Under 55 years – ASA I/II) | Continuous infusion of Pofol at a rate of 0.1-0.2 mg/kg/minute through IV to maintain the anesthesia during surgery. |
| Anesthesia Maintenance for Adults (Over 55 years or debilitated – ASA III/IV) | Lower maintenance dosage of 0.05-0.1 mg/kg/minute through IV to ensure safe and controlled anesthesia. |
| Maintenance for Pediatric Patients (2 months – 16 years – ASA I/II) | Pediatric patients receive Pofol at 0.125-0.3 mg/kg/minute through IV to adapt to their unique needs. |
| MAC Sedation Initiation | Pofol administered at a rate of 0.1-0.15 mg/kg/minute through IV for 3-5 minutes, adjusting based on the desired sedation effect. |
| ICU Sedation Initiation | Slowly introduce Pofol at 0.005 mg/kg/minute through IV for at least 5 minutes to achieve the desired sedation level. |
| ICU Sedation Maintenance | Individualized dosage maintenance ranging from 0.005-0.05 mg/kg/minute through IV, adjusted based on the patient’s response. |
| Postoperative Nausea/Vomiting | Post-surgery, 20 mg of Pofol can be administered through IV, with the option to repeat if necessary. |
Pofol Side Effects – Stay Informed for a Safe Experience!
- Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension): A common side effect where the blood pressure decreases, potentially causing dizziness.
- Pauses in Breathing (Apnea): Temporary halts in breathing lasting either 30-60 seconds or more than 60 seconds, a known occurrence associated with Pofol use.
- Movement: Some individuals may experience involuntary movements during or after receiving Pofol.
- Injection Site Discomfort: A localized side effect characterized by sensations of burning, stinging, or pain at the site where Pofol is administered.
- Respiratory Acidosis During Weaning: The blood becomes too acidic due to inadequate breathing while discontinuing Pofol.
- Hypertriglyceridemia: An increase in the levels of triglycerides (a type of fat in the blood), which might pose a risk to cardiovascular health.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): While less common, an elevation in blood pressure can occur as a side effect of Pofol use.
- Rash and Itching: Skin reactions like rashes and itching may occur in response to Pofol.
- Irregular Heartbeat (Arrhythmia): Pofol use might lead to changes in the normal heart rhythm, resulting in an irregular heartbeat.
- Slow or Fast Heart Rate: Pofol can influence heart rate, causing it to slow down or speed up.
- Less Common Side Effects: These include arterial hypotension, severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), cardiac “flatline” (asystole), bronchospasm, cardiac arrest, seizures, inner ear reactions, pancreatitis, fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema), phlebitis, blood clot, and renal tubular toxicity.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Is Pofol safe for everyone?
Pofol should be used with caution in individuals with asthma, bleeding disorders, cardiac disease, hepatic impairment, hypertension, or renal impairment. Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals should consult with healthcare providers before its use.
2. Can Pofol be abused?
Yes, there have been reports of Pofol abuse for recreational purposes, leading to fatalities. Proper inventory control and restrictions on access are crucial to prevent misuse.
3. What is Propofol infusion syndrome?
Propofol infusion syndrome is a rare but severe condition associated with prolonged, high-dose infusions of Pofol. It can lead to metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia, lipemia, rhabdomyolysis, hepatomegaly, and potential cardiac and renal failure.
4. How is Pofol administered?
Pofol is administered through intravenous (IV) injection or infusion. The dosage and administration method depends on age, health condition, and medical situation.
5. What precautions should be taken with Pofol?
Precautions include careful management of discontinuation to avoid anxiety and agitation, monitoring for cardiovascular and respiratory effects, and considering the potential risks of long-term exposure, especially in pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Conclusion:
Pofol is like sleepy superhero doctors use during surgeries and medical procedures to comfort us. While it helps, it’s crucial to remember possible side effects and follow the guidance of healthcare experts for a safe experience.
Also Read: